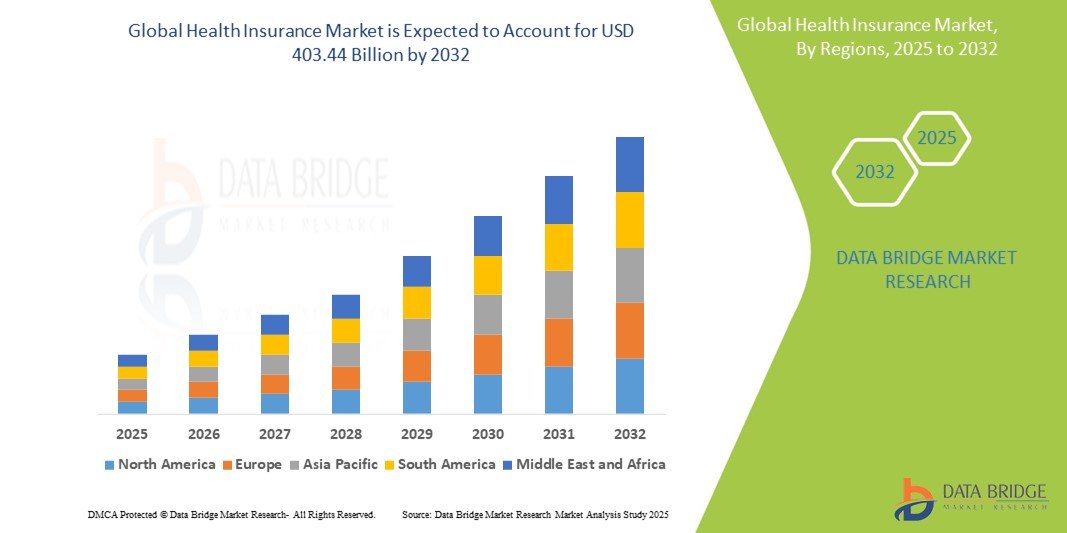
Introduction
The health insurance market stands as one of the most crucial pillars of the global healthcare system. With rising healthcare costs, unpredictable medical emergencies, and the increasing demand for accessible treatment, health insurance has become an essential safety net for individuals, families, corporations, and even governments. Moreover, it not only provides financial protection but also improves access to healthcare services, thereby ensuring healthier populations and stronger economies.
In addition, the health insurance market is no longer limited to basic hospitalization coverage. Today, it includes a wide variety of policies, ranging from comprehensive medical plans and critical illness insurance to wellness-focused programs and telemedicine integration. Consequently, insurers have had to innovate continuously to address diverse customer needs, adapt to regulatory changes, and respond to shifting economic realities.
Furthermore, as global awareness around health and wellness rises, consumers are increasingly demanding transparency, affordability, and customization. Therefore, understanding the evolution, market trends, challenges, scope, size, and the major growth drivers of this industry is essential for appreciating its significance in the modern world.
Source: https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-health-insurance-market
The Evolution of the Health Insurance Market
The concept of health insurance has evolved over centuries, transitioning from simple mutual aid societies to sophisticated, technology-driven financial products. Initially, in the early stages, healthcare costs were managed through community-based risk-sharing mechanisms. However, as medical science advanced and treatments became more expensive, the need for structured financial protection grew stronger.
In the 19th and early 20th centuries, the first formal health insurance schemes began to emerge, especially in industrialized countries. These were primarily employer-based programs designed to protect workers against medical expenses and income loss due to illness. Gradually, governments recognized the need for wider coverage, leading to the establishment of public health insurance programs and, in some regions, the foundation of universal healthcare systems.
Moreover, the post-World War II period saw rapid expansion of both private and public insurance systems. As healthcare infrastructure developed, insurance became not only a safety measure but also a mechanism to drive greater utilization of medical services. Consequently, this period laid the foundation for the modern health insurance sector.
In addition, the rise of private insurers and global corporations in the late 20th century further diversified the industry. Companies began offering tailored insurance products, catering to individuals, families, and corporate groups with different income levels and health needs.
Today, the health insurance market is at a new stage of transformation, powered by digital technologies, data-driven solutions, and personalized health plans. Artificial intelligence, predictive analytics, and telehealth are shaping how insurers design products and interact with policyholders. Therefore, the evolution of the health insurance market highlights a remarkable journey—from simple financial assistance to a comprehensive, technology-driven ecosystem that prioritizes both health outcomes and financial security.
Market Trends
The health insurance market is experiencing a variety of dynamic trends that are reshaping the way policies are designed, delivered, and consumed.
-
Digital Transformation and InsurTech
Mobile apps, artificial intelligence, and blockchain are being used to streamline claims processing, enhance transparency, and provide real-time policy management. Consequently, customer experiences are becoming more seamless. -
Shift Toward Preventive Healthcare
Insurers are increasingly incorporating wellness programs, gym memberships, mental health support, and preventive screenings into their products. Moreover, this not only reduces long-term costs but also promotes healthier lifestyles. -
Customized and Modular Plans
Consumers are demanding flexibility, leading to the rise of customizable health insurance packages. As a result, policyholders can add or remove benefits according to their specific needs and budgets. -
Telemedicine Integration
Telehealth has become a key component of many insurance plans, providing policyholders with access to virtual consultations. Furthermore, this trend has accelerated post-pandemic and continues to grow. -
Corporate and Group Insurance Expansion
Employers are increasingly offering health benefits to attract and retain talent. In addition, group policies provide cost-effective solutions for employees and promote productivity by ensuring healthier workforces. -
Growing Role of Public-Private Partnerships
Governments are collaborating with private insurers to expand coverage, particularly in developing countries. Consequently, this trend is bridging the gap between public healthcare and private access. -
Focus on Mental Health Coverage
Rising awareness of mental health issues has encouraged insurers to include counseling, therapy, and psychiatric care in their policies. Moreover, this marks a shift from physical health-only coverage. -
Adoption of Value-Based Insurance Models
Instead of focusing solely on claim reimbursement, insurers are moving toward models that reward better health outcomes and cost efficiency.
Altogether, these trends indicate that the health insurance market is not only growing but also transforming into a holistic health ecosystem.
Challenges in the Health Insurance Market
Despite its growth, the health insurance market faces several challenges that affect providers, policymakers, and consumers alike.
-
High Premium Costs
Rising medical expenses, coupled with inflation and advanced treatment technologies, often lead to higher insurance premiums. Consequently, affordability remains a major concern. -
Lack of Awareness and Understanding
Many individuals still struggle to understand insurance terms, benefits, and exclusions. Moreover, misinformation and lack of education create barriers to adoption. -
Fraud and Mismanagement
Insurance fraud, ranging from false claims to identity theft, continues to be a significant issue, leading to increased costs and stricter regulations. -
Regulatory Complexities
Each country has its own set of insurance regulations, which can make global operations and product standardization difficult. -
Healthcare Accessibility Inequality
In many developing regions, even insured individuals face limited access to quality healthcare facilities, undermining the benefits of coverage. -
Customer Expectations for Transparency
Customers increasingly expect quick claims settlements and clear communication. Failure to meet these expectations can lead to dissatisfaction and reputational harm. -
Impact of Pandemics and Global Crises
Events like COVID-19 highlight vulnerabilities in the system, leading to higher claims, financial strain, and changes in risk assessment models.
Nevertheless, each of these challenges presents opportunities for innovation, policy reform, and technological intervention.
Market Scope
The scope of the health insurance market is vast and diverse, covering a wide range of policy types and applications.
-
Individual Health Insurance: Policies purchased by individuals or families for personal coverage.
-
Group Health Insurance: Employer-provided plans that cover employees and sometimes their dependents.
-
Critical Illness Insurance: Coverage for life-threatening conditions such as cancer, heart disease, or stroke.
-
Senior Citizen Plans: Specially designed policies catering to older populations with specific health needs.
-
International Health Insurance: Plans designed for expatriates and frequent travelers.
-
Supplemental Health Insurance: Add-ons covering expenses not included in basic policies, such as dental, vision, or maternity.
-
Micro-Insurance Schemes: Low-cost policies targeting underserved and rural populations in emerging markets.
Therefore, the health insurance market has the flexibility to serve both developed and developing economies, catering to diverse income levels, health risks, and consumer preferences.
Market Size and Factors Driving Growth
The health insurance market has grown into a multi-trillion-dollar industry worldwide, and projections suggest strong expansion over the next decade. Several key factors are driving this growth:
-
Rising Healthcare Costs
With advanced medical technologies and longer life expectancies, healthcare expenses continue to rise, making insurance essential. -
Growing Middle-Class Population
Emerging economies are witnessing a rapidly expanding middle class that demands better healthcare access and financial protection. -
Government Initiatives
Many governments are introducing mandatory health insurance schemes, subsidies, and incentives to increase coverage. -
Increasing Awareness of Preventive Healthcare
Rising health consciousness is pushing individuals to secure insurance not only for emergencies but also for wellness programs. -
Technological Advancements
Digital platforms, AI-driven claims processing, and telemedicine are making health insurance more accessible and efficient. -
Pandemic-Driven Demand
The COVID-19 crisis underscored the importance of financial protection against medical emergencies, leading to a surge in new policies. -
Aging Population
With the global population aging, there is growing demand for senior-focused insurance products. -
Corporate Demand
Employers worldwide are offering comprehensive health coverage to retain employees and improve workplace productivity.
Consequently, these drivers ensure the continued expansion of the health insurance industry across regions and demographics.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the health insurance market has undergone a profound transformation from its early beginnings as a mutual aid concept to a modern, technology-driven industry. Its evolution, shaped by digital innovation, regulatory frameworks, and consumer demands, reflects its critical role in global healthcare systems.
Moreover, trends such as telemedicine integration, preventive health programs, customized policies, and InsurTech innovations are reshaping the future of health insurance. At the same time, challenges such as affordability, regulatory hurdles, and fraud require strategic solutions.
Nevertheless, the scope of the market remains vast, with opportunities in both developed and emerging regions. Consequently, the health insurance industry is not only growing in size but also becoming an essential enabler of financial protection, healthcare accessibility, and long-term population well-being.
Therefore, the health insurance market is positioned to continue expanding, shaping healthier societies and stronger economies around the world.